Photo by Domenico Loia on Unsplash
Sailing Smoothly in Binary Tree Territory
Avoiding Traps and Triumphing in Implementation of Binary Trees.
Table of contents
No headings in the article.
Binary trees are powerful data structures but can be tricky to work with, especially for those new to them. This blog post will dive into the common pitfalls and mistakes that we (developers) often encounter when working with binary trees. By highlighting these challenges, readers will gain a better understanding of potential stumbling blocks and learn how to avoid or overcome them effectively.
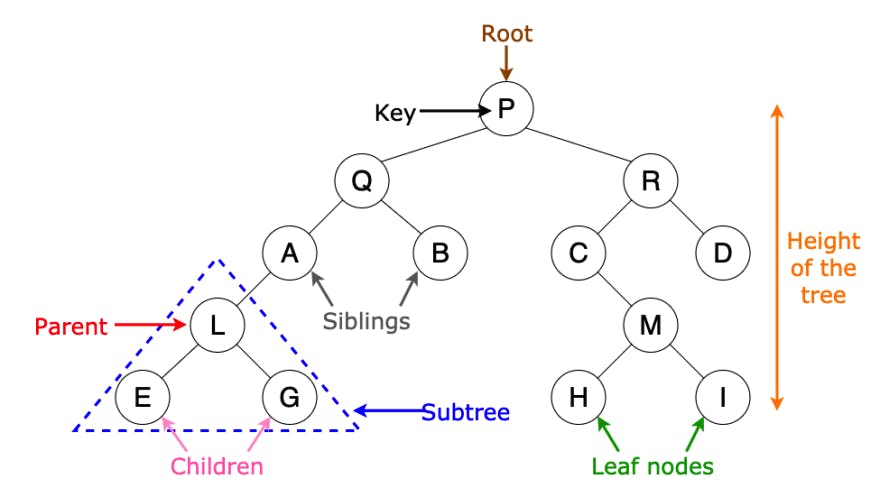
Understanding Binary Trees: Binary trees are hierarchical data structures consisting of nodes connected through parent-child relationships. Each node can have at most two children: a left child and a right child. The topmost node is called the root node, while nodes with no children are called leaf nodes. Understanding these fundamental concepts is key to working with binary trees effectively.
Building a Binary Tree: To build a binary tree, you start with a root node and add nodes in a specific order. Each new node is inserted as either the left or right child of an existing node. By following this process recursively, you construct the desired binary tree. Visualizing the tree structure using diagrams can greatly aid in understanding and building the tree correctly.
Traversing a Binary Tree: Tree traversal refers to the process of visiting each node in the tree in a specific order. There are three common traversal techniques:
In-order traversal: Visit the left subtree, then the root, and finally the right subtree.
Pre-order traversal: Visit the root, then the left subtree, and finally the right subtree.
Post-order traversal: Visit the left subtree, then the right subtree, and finally the root.
Recursive and iterative approaches can be used to implement these traversal techniques, each with its own benefits and trade-offs. Understanding and implementing tree traversal is crucial for many tree-based algorithms.
Searching in a Binary Tree: Binary trees provide an efficient way to search for specific values. The binary search algorithm exploits the properties of a binary search tree (BST), where values in the left subtree are smaller than the root and values in the right subtree are larger. By recursively comparing the target value with the current node, you can efficiently navigate the tree and find the desired value. The time complexity of searching in a binary tree is O(log n) in average and O(n) in the worst case.
Inserting and Deleting Nodes: To insert a new node into a binary tree, you need to find the appropriate position according to the node's value and adjust the links accordingly. The process involves comparing values and traversing the tree until you find an empty spot to insert the new node. Deleting a node requires adjusting the links to maintain the structure of the tree. Special cases, such as removing a node with children, need to be handled carefully to preserve the integrity of the tree.
Balancing Binary Trees: Balancing a binary tree ensures that the tree remains efficient for various operations. Unbalanced trees can lead to degraded performance, making operations slower. Self-balancing binary trees, such as AVL trees, automatically adjust their structure during insertions and deletions to maintain balance. These balanced trees offer better time complexity guarantees, ensuring efficient operations even in the worst-case scenarios.
Common Mistakes to Avoid: When working with binary trees, beginners often encounter common mistakes. Some pitfalls to be aware of include incorrectly placing nodes, not considering special cases during insertion and deletion, and neglecting memory management, which can lead to memory leaks. By understanding these potential pitfalls, you can avoid them and build robust and error-free binary tree implementations.
Tips for Success: To succeed in working with binary trees, it's important to follow these tips:
Write clean and modular code to enhance readability and maintainability.
Test your binary tree implementations thoroughly, including edge cases.
Debug any issues that arise during implementation or testing.
Utilize available resources, such as textbooks, online tutorials, and coding communities, to deepen your understanding of binary trees.
Practical Applications: Binary trees find applications in various domains. For example:
File systems: Binary trees can represent the hierarchical structure of directories and files.
Hierarchical data: They are used to represent organization charts, family trees, and XML/HTML parsing.
Binary search: Binary search trees enable efficient searching in sorted data.
Understanding these practical applications helps solidify your understanding of binary trees and showcases their usefulness in solving real-world problems.
By following this beginner's guide, you have gained a solid understanding of binary trees and how to navigate their implementations successfully. Remember to start with a clear understanding of the basics, construct the tree correctly, implement traversal techniques, and be mindful of potential pitfalls. Through practice and exploration, you'll become more comfortable and confident in working with binary trees, unlocking their full potential in your programming journey. Happy sailing in the fascinating world of binary tree territory
